Prostate Enlargement
- Home
- Prostate Enlargement
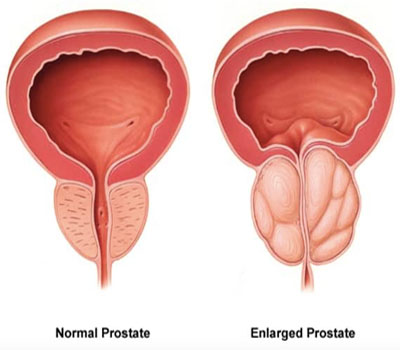
Prostate Enlargement
Prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition in aging men. It involves the non-cancerous growth of the prostate gland, which is a part of the male reproductive system. Here are some key points about prostate enlargement:
Symptoms:
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate.
- Difficulty starting or maintaining urination.
- Weak urine stream.
- Dribbling at the end of urination.
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Nocturia (frequent urination at night).
Causes:
- The exact cause is not well understood, but age and changes in the balance of sex hormones are believed to play a role.
- Testosterone and its byproduct dihydrotestosterone (DHT) contribute to prostate growth.
Diagnosis:
- Medical history and physical examination.
- Digital rectal exam (DRE) to assess the size and condition of the prostate.
- Urinalysis to check for urinary tract infections or other issues.
Treatment:
- Watchful waiting: Monitoring the condition without immediate intervention.
- Medications: Alpha-blockers or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors to relax the prostate muscles or shrink the prostate.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), laser therapy, or other techniques to remove or reduce excess prostate tissue.
- Surgery: In severe cases, open or robotic-assisted prostatectomy may be recommended.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the evening.
- Timed voiding: Scheduled bathroom trips to prevent overfilling of the bladder.
- Kegel exercises to strengthen pelvic floor muscles.
It's essential for individuals experiencing symptoms of prostate enlargement to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan. Regular check-ups and open communication with a doctor are crucial for monitoring and addressing any changes in prostate health.